
Describing Data Year 5 Statistics Lesson by PlanBee
(With Examples) Written by Coursera Staff • Updated on Nov 20, 2023 Data analysis is the practice of working with data to glean useful information, which can then be used to make informed decisions. "It is a capital mistake to theorize before one has data.

Describing charts Writing Intermediate B1 British Council
Statistics and probability 16 units · 157 skills. Unit 1 Analyzing categorical data. Unit 2 Displaying and comparing quantitative data. Unit 3 Summarizing quantitative data. Unit 4 Modeling data distributions. Unit 5 Exploring bivariate numerical data. Unit 6 Study design. Unit 7 Probability. Unit 8 Counting, permutations, and combinations.

Great How To Write Report Based On Bar Chart A Qualitative Data Analysis
There are 3 main types of descriptive statistics: The distribution concerns the frequency of each value. The central tendency concerns the averages of the values. The variability or dispersion concerns how spread out the values are.

SOLUTION Describing data Studypool
These calculations provide descriptive statistics that summarize the central tendency, dispersion, and shape of the data in these examples. Types of Descriptive Statistics. Descriptive statistics break down into several types, characteristics, or measures. Some authors say that there are two types. Others say three or even four.

Describing Data Year 5 Statistics Lesson by PlanBee
Descriptive statistics are brief descriptive coefficients that summarize a given data set, which can be either a representation of the entire population or a sample of it. Descriptive statistics.

Describing Data Year 5 Statistics Lesson by PlanBee
It may include full definitions of any abbreviations used, units of measurement, allowable values in a field, data types, thesauri or controlled vocabularies used, and other important details of the data elements along with a brief description of the provenance or parameters of the data, i.e., date or location the data was collected.
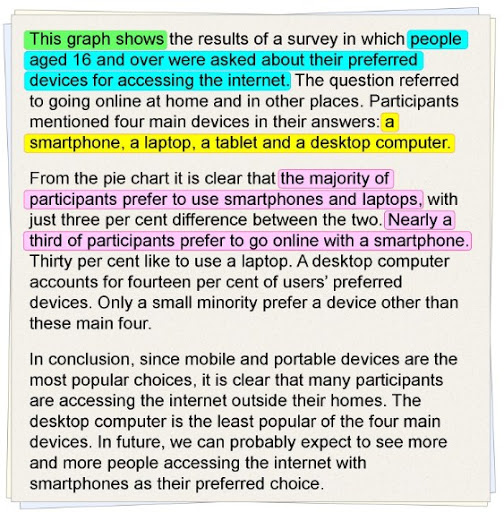
How to describe charts, graphs, and diagrams in the presentation
2 Describing and Summarizing Data Chris Bailey, PhD, CSCS, RSCC This chapter will discuss ways in which we can summarize and describe our data. This is often done with descriptive statistics, where we describe the central tendency of the data as well as it's variability.

Describing Data Year 5 Statistics Lesson by PlanBee
Data-driven decision-making also depends on how efficiently we use these methods. Two types of statistical methods are widely used in data analysis: descriptive and inferential. This article will focus more on descriptive statistics, its types, calculations, examples, etc. This article was published as a part of the Data Science Blogathon.

Total 112+ imagen vocabulary for bar chart Expoproveedorindustrial.mx
Example 1: Descriptive statistics about a college involve the average math test score for incoming students. It says nothing about why the data is so or what trends we can see and follow. Descriptive statistics help you to simplify large amounts of data in a meaningful way. It reduces lots of data into a summary. Example 2:
PPT Chapter 2. Describing Data PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1247600
Figure 1 - Data Labels Figure 1: The first chart lacks data labels to help users decipher the content. By contrast, the second chart contains data labels for each of the series data points. Provide Text Descriptions or Data Tables for Graphics With your data labels on your charts and graphs, visual users can more easily interpret the content.

Informal Letter Writing, Ielts Writing Academic, English Letter Writing, Essay Writing Skills
Data analytics can be broken into four key types: Descriptive, which answers the question, "What happened?" Diagnostic, which answers the question, "Why did this happen?" Predictive, which answers the question, "What might happen in the future?" Prescriptive, which answers the question, "What should we do next?"

graphème en francais
Some important examples are: Mean, median and mode Range and interquartile range Quartiles and percentiles Standard deviation and variance Note: Descriptive statistics is often presented as a part of statistical analysis.
Describing Data
Perhaps the most straightforward of them is descriptive analysis, which seeks to describe or summarize past and present data, helping to create accessible data insights. In this short guide, we'll review the basics of descriptive analysis, including what exactly it is, what benefits it has, how to do it, as well as some types and examples. Contents

PPT CS1001 XML and Applications PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2492099
Examples are provided for writing a data description, including how to reference the source of the data, describe methods used to collect the data, summarize how the data were cleaned and prepared, and provide information about the variables used in the analysis. This chapter also provides tips on how to present summary statistics.

Describing Data Year 5 Statistics Lesson by PlanBee
Examples of Descriptive Statistics Udemy Editor Share this article In statistics, data is everything. When you collect your data, you can make a conclusion based on how you use it. Calculating things, such as the range, median, and mode of your set of data is all a part of descriptive statistics.

Describing Data Year 5 Statistics Lesson by PlanBee
8 min read · Jul 21, 2020 -- 1 Descriptive comes from the word 'describe' and so it typically means to describe something. Descriptive statistics is essentially describing the data through methods such as graphical representations, measures of central tendency and measures of variability.